Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations (SOR/2012-167)
Full Document:
- HTMLFull Document: Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations (Accessibility Buttons available) |
- XMLFull Document: Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations [228 KB] |
- PDFFull Document: Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations [531 KB]
Regulations are current to 2024-10-30 and last amended on 2018-11-30. Previous Versions
PART 2Reporting, Sending, Recording and Retention of Information
Marginal note:Annual report
15 For each calendar year, a responsible person for each of the following units must, on or before June 1 that follows that calendar year, send an annual report to the Minister that contains the information set out in Schedule 4:
(a) a new unit;
(b) an old unit;
(c) a substituted unit referred to in subsection 5(5);
(d) an existing unit referred to in subsection 14(1), if that calendar year is a calendar year included in the remaining portion of the seven consecutive calendar years referred to in subsection 14(5).
Marginal note:Electronic report, notice and application
16 (1) A report or notice that is required, or an application that is made, under these Regulations must be sent electronically in the form and format specified by the Minister and must bear the electronic signature of an authorized official of the responsible person.
Marginal note:Paper report or notice
(2) If the Minister has not specified an electronic form and format or if it is impractical to send the report, notice or application electronically in accordance with subsection (1) because of circumstances beyond the person’s control, the report, notice or application must be sent on paper, signed by an authorized official of the responsible person, and in the form and format specified by the Minister. However, if no form and format have been so specified, it may be in any form and format.
Marginal note:Record-making
17 (1) A responsible person for a unit must make a record
(a) of any notice referred to in subsection 4(3), 5(6) or 6(6) or section 12 that was sent to the Minister and the information that was contained in it, as well as any supporting documents;
(b) of any application referred to in subsection 5(3), 6(3), 7(3), 8(2), 9(2) or 14(3) and the information referred to in the subsection, as well as any supporting documents;
(c) of every direct measure of the flow of, and the concentration of CO2 in, emissions referred to in paragraph 14(1)(e), subsection 20(2) and the descriptions of Enon-ccs in subsection 21(1) and of Eccs in section 22;
(d) of every measurement and calculation used to determine a value of an element of a formula set out in any of sections 19 and 21 to 24;
(e) that demonstrates that any meter referred to in section 19 complies with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations, including a certificate referred to in section 14 of that Act;
(f) for each calendar year during which a responsible person used a continuous emission monitoring system referred to in paragraph 20(1)(a), of any document, record or information referred to in section 8 of the Reference Method;
(g) that demonstrates that the installation, maintenance and calibration of measuring devices referred to in subsection 25(1) was in accordance with that subsection and subsection 25(3) and of every calibration referred to in subsection 25(2); and
(h) of the results of the analysis of every sample collected in accordance with section 27.
Marginal note:When records made
(2) Records referred to in paragraphs (1)(c) to (h) must be made as soon as feasible but not later than 30 days after the information to be recorded becomes available.
Marginal note:Retention of records and reports
18 (1) A responsible person who is required under these Regulations to make a record or send a report or notice must keep the record or a copy of the report or notice, as well as any supporting documents that relate to the information contained in that record or copy, for at least seven years after they make the record or send the report or notice. The record or copy must be kept at the person’s principal place of business in Canada or at any other place in Canada where it can be inspected. If the record or copy is kept at any of those other places, the person must provide the Minister with the civic address of that other place.
Marginal note:Change of address
(2) If the civic address referred to in subsection (1) changes, the responsible person must notify the minister in writing within 30 days after the change.
PART 3Quantification Rules
Production of Electricity
Marginal note:Electricity
19 (1) The quantity of electricity referred to in paragraph 3(2)(a) is to be determined in accordance with the following formula:
Ggross – Gaux
where
- Ggross
- is the gross quantity of electricity that is produced by the unit during the calendar year, expressed in GWh and measured at the electrical terminals of the generators of the unit using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations; and
- Gaux
- is the quantity of electricity that is produced by the unit and used by the power plant in which the unit is located during the calendar year to operate infrastructure and equipment that is attributed to the unit for electricity generation and for separation, but not for pressurization, of CO2, expressed in GWh, determined in accordance with an appropriate method of attribution, based on data collected using meters that comply with the requirements of the Electricity and Gas Inspection Act and the Electricity and Gas Inspection Regulations.
Marginal note:Same method of attribution in subsequent years
(2) Once a method of attribution is used to make the determination referred to in the description of Gaux for a calendar year, that method of attribution must be used to make that determination for every subsequent calendar year, unless
(a) during a subsequent calendar year, a unit located at the power plant ceases to produce electricity or a new unit is added to those located at the power plant; or
(b) during a subsequent calendar year, the operation of any unit located at the power plant is integrated with a carbon capture and storage system.
Marginal note:Change of method of attribution
(3) If paragraph (2)(a) or (b) applies in a subsequent calendar year, the responsible person must, when making the determination referred to in the description of Gaux in subsection (1) for that subsequent calendar year, use a method of attribution that is appropriate to the circumstances described in that paragraph. Subsection (2) applies in respect of that appropriate method of attribution and that subsequent calendar year as if they were, respectively, the method of attribution and the calendar year referred to in that subsection.
- SOR/2018-263, s. 8
CO2 Emissions
Means of Quantification
Marginal note:CEMS or fuel-based methods
20 (1) For the purposes of sections 3 and 15, the quantity of CO2 emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels in a unit for a calendar year is to be determined
(a) by using a continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS) in accordance with section 21; or
(b) by using a fuel-based method, based on the quantity of carbon in the fossil fuel fed for combustion, in accordance with section 22 and section 23 or 24.
Marginal note:Emissions from coal gasification systems
(2) If a coal gasification system referred to in subsection 3(4) is used to produce fuel for a unit, the quantity of emissions from the unit referred to in subsection (1) must be determined in accordance with paragraph (1)(a). To the extent that the emissions from the coal gasification system are not captured, transported and stored as described in subsection 3(5), that quantity must be determined for the purpose of subsection 3(1) by using a direct measure of the flow of, and the concentration of CO2 in, those emissions.
Continuous Emissions Monitoring System
Marginal note:Quantification
21 (1) If paragraph 20(1)(a) applies, the quantity of CO2 emissions referred to in subsection 20(1) is to be determined in accordance with the following formula:
Eu – Ebio + Enon-ccs
where
- Eu
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the unit, “u”, during the calendar year from the combustion of fuel, as measured by the CEMS in accordance with sections 7.1 to 7.7 of the Reference Method;
- Ebio
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year, determined
(a) by using a fuel-based method
(i) in accordance with paragraph 24(1)(a) or (b), if the unit combusts solid biomass at an average daily rate of less than 3t/day during the given calendar year, and
(ii) in accordance with the applicable formula set out in one of paragraphs 23(1)(a) to (c) for the type of biomass combusted, in any other case, or
(b) by using the method, based on data from the CEMS, described in subsection (2); and
- Enon-ccs
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the combustion of fuel in the unit, including those emissions referred to in subsection 3(4), during the calendar year — other than the quantity of those emissions as measured by the CEMS and set out in the description of Eu — that is determined using a direct measure of the flow of, and the concentration of CO2 in, the emissions from that combustion of fuel but that is not ultimately captured, transported and stored as described in subsection 3(5).
Marginal note:Ebio based on CEMS data
(2) For the purpose of determining the value of Ebio, the method, based on data from the CEMS, consists of making the following sequence of determinations:
(a) the volume of CO2 emitted from combustion of fuel in the unit for each hour of production of electricity during the calendar year determined in accordance with the following formula:
0.01 × %CO2w,h × Qw,h × th
where
- %CO2w,h
- is the average concentration of CO2 in relation to all gases in the stack emitted from the combustion of fuel in the unit during a given hour, “h”, during which the unit produced electricity in the calendar year — or, if applicable, a calculation made in accordance with section 7.4 of the Reference Method of that average concentration of CO2 based on a measurement of the concentration of oxygen (O2) in those gases in the stack — expressed as a percentage on a wet basis,
- Qw,h
- is the average volumetric flow during that hour, measured on a wet basis by the stack gas volumetric flow monitor, expressed in standard m3, and
- th
- is the period during which the unit produced electricity, expressed in hours;
(b) the volume of CO2 emitted from combustion of fossil fuel in the unit during the calendar year, expressed in standard m3 and referred to in this subsection as Vff, determined in accordance with the following formula:
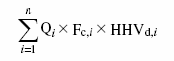
where
- Qi
- is the quantity of fossil fuel type “i” combusted in the unit during the calendar year, determined
(a) for a solid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Mf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(a) and expressed in tonnes,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(b) and expressed in kL, and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(c) and expressed in standard m3,
- i
- is the ith fossil fuel type combusted in the unit during the calendar year, with “i” going from the number 1 to n, where n is the number of fossil fuels so combusted,
- Fc,i
- is the fuel-specific carbon-based F-factor for each fossil fuel type “i” — being, as the case may be, the default value as set out in column 3 of the table to subsection (3) for that fuel type set out in column 2 or determined for that fuel type in accordance with Appendix A of the Reference Method — expressed in standard m3 of CO2/GJ,
- HHVd,i
- — expressed in GJ/tonne, for a solid fuel, in GJ/kL, for a liquid fuel, and in GJ/standard m3, for a gaseous fuel — is, for each fossil fuel type “i”,
(a) the default higher heating value set out in column 2 of Schedule 5 for that fuel type set out in column 1, and
(b) in the absence of a default higher heating value for that fuel type referred to in paragraph (a), a default higher heating value for that fuel type established by a body that is internationally recognized as being competent to establish default higher heating values for fuels;
(c) the volume of CO2 emitted from the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year, expressed in standard m3 and referred to in this subsection as Vbio, determined in accordance with the following formula:
VT – Vff
where
- VT
- is the sum of the volumes of CO2 emitted from combustion of fuel in the unit during each hour of production of electricity during the calendar year, as determined under paragraph (a), and
- Vff
- is Vff determined in accordance with the formula set out in paragraph (b); and
(d) the quantity of the CO2 emissions from the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year, namely Ebio determined in accordance with the formula set out in subsection (1), based on the following two determinations:
(i) the fraction of the volume of CO2 emissions from all fuel combusted in the unit attributable to the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year, referred to in this section as Biofr, determined in accordance with the following formula:
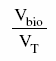
where
- Vbio
- is the volume of CO2 emitted from the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year determined in accordance with the formula set out in paragraph (c),
- VT
- is the value of VT determined in accordance with the formula set out in paragraph (c), and
(ii) the quantity of CO2 emissions described by Ebio determined in accordance with the following formula:
(Biofr× Eu) – Es
where
- Biofr
- is the fraction of the volume of CO2 emissions from all fuel combusted in the unit attributable to the combustion of biomass in the unit during the calendar year determined in accordance with the formula set out in subparagraph (i),
- Eu
- is the value of Eu determined in the formula set out in subsection (1), and
- Es
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, that is released from the use of sorbent to control the emission of sulphur dioxide from the unit during the calendar year, determined in accordance with the following formula:
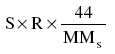
where
- S
- is the quantity of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) or other sorbent material so used, expressed in tonnes,
- R
- is the stoichiometric ratio, on a mole fraction basis, of CO2 released on usage of one mole of sorbent material, where R=1 if the sorbent material is CaCO3, and
- MMs
- is the molecular mass of the sorbent material, where MMs = 100 if the sorbent material is CaCO3.
Marginal note:Default F-factor
(3) The default value for the fuel-specific carbon-based F-factor for certain types of fossil fuel is set out in column 3 of the following table:
TABLE
Column 1 Column 2 Column 3 Item Fossil fuel Type F-factor (standard m3/GJ) 1 Coal Anthracite 54.2 Bituminous 49.2 Sub-bituminous 49.2 Lignite 53.0 2 Oil Crude, residual or distillate 39.3 3 Gas Natural 28.4 Propane 32.5 Marginal note:Common stack — disaggregation
(4) Despite subsection (1), if there is one or more other units at a power plant where a unit is located and a CEMS measures emissions from that unit and from one or more of those other units at a common stack rather than at the exhaust duct of that unit and of each of those other units that brings those emissions to the common stack, then the quantity of emissions attributable to that unit for the purpose of subsection (1) is determined based on the ratio of the heat input of that unit to the total of the heat input of that unit and of all of those other units sharing the common stack in accordance with the following formula:
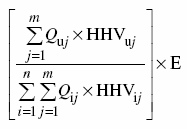
where
- Quj
- is the quantity of fuel type “j” combusted in that unit “u” during the calendar year, determined
(a) for a solid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Mf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(a) and expressed in tonnes,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(b) and expressed in kL, and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, in the same manner as the one used in the determination of Vf in the formula set out in paragraph 23(1)(c) and expressed in standard m3;
- HHVuj
- is the higher heating value, determined in accordance with section 24 and expressed in the applicable unit of measure referred to in that section of fuel type “j” combusted during the calendar year in that unit “u”;
- i
- is the ith unit located at the power plant with “i” going from the number 1 to n, where n is the number of units that share a common stack;
- j
- is the jth fuel type, including types of biomass, combusted during the calendar year in a unit located at the power plant with “j” going from the number 1 to m, where m is the number of those fuel types;
- Qij
- is the quantity of fuel type “j” combusted in each unit “i” during the calendar year, determined for a solid fuel, a liquid fuel and a gaseous fuel, respectively, in the manner set out in the description of Quj;
- HHVij
- is the higher heating value, determined in accordance with section 24 and expressed in the applicable unit of measure referred to in that section, of fuel type “j” combusted during the calendar year in unit “i”; and
- E
- is the quantity of CO2 emissions, expressed in tonnes, from the combustion of fuels in all the units during the calendar year, measured by a CEMS at the common stack in accordance with subsection 21(1).
- Date modified: