Reduction of Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Coal-fired Generation of Electricity Regulations
Marginal note:Measured carbon content
23 (1) Subject to section 24, the quantity of CO2 emissions attributable to the combustion of a fuel in a unit during a calendar year, expressed in tonnes, is determined in accordance with the applicable formula, as follows:
(a) for a solid fuel
Mf × CCA × 3.664
where
- Mf
- is the mass of the fuel combusted during the calendar year as determined, as the case may be, on a wet or dry basis, expressed in tonnes and measured by a measuring device, and
- CCA
- is the weighted average, expressed in kg of carbon per kg of the fuel, of the carbon content of the fuel determined in accordance with subsection (2) on the same wet or dry basis as the one used in the determination of Mf;
(b) for a liquid fuel
Vf × CCA × 3.664
where
- Vf
- is the volume of the fuel combusted during the calendar year, expressed in kL, determined by using flow meters, and
- CCA
- is the weighted average, expressed in tonnes of carbon per kL of the fuel, of the carbon content of the fuel determined in accordance with subsection (2) at the same temperature as the one used in the determination of Vf; and
(c) for a gaseous fuel
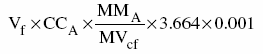
where
- Vf
- is the volume of the fuel combusted during the calendar year, expressed in standard m3, determined by using flow meters,
- CCA
- is the weighted average, expressed in kg of carbon per kg of the fuel, of the carbon content of the fuel determined in accordance with subsection (2),
- MMA
- is the average molecular mass of the fuel, expressed in kg per kg-mole of the fuel, determined based on fuel samples collected in accordance with section 27, and
- MVcf
- is the molar volume conversion factor, namely 23.645 standard m3 per kg-mole of the fuel at standard conditions of 15°C and 101.325 kPa.
Marginal note:Weighted average
(2) The weighted average referred to in paragraphs (1)(a) to (c) as CCA is, based on fuel samples collected in accordance with section 27, to be determined in accordance with the following formula:
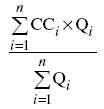
where
- CCi
- is the carbon content of, as the case may be, the composite sample, or the sample, of the fuel for the ith sampling period expressed for solid fuels, liquid fuels and gaseous fuels, respectively, in the same unit of measure as the one set out in CCA, as provided by the supplier of the fuel to the responsible person and, if not so provided, as determined by the responsible person, and measured
(a) for a solid fuel, on the same wet or dry basis as the one used in the determination of CCA, in accordance with,
(i) for coal, biomass or solid fuel derived from waste, ASTM D5373 - 08, entitled Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Laboratory Samples of Coal, and
(ii) for any other solid fuel,
(A) an applicable ASTM standard for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel, and
(B) if no such ASTM standard applies, an applicable internationally recognized method for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in accordance with any of the following standards or methods that applies for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel:
(i) ASTM D3238 - 95(2010), entitled Standard Test Method for Calculation of Carbon Distribution and Structural Group Analysis of Petroleum Oils by the n-d-M Method, along with either of the following applicable ASTM standards:
(A) ASTM D2503 - 92(2007), entitled Standard Test Method for Relative Molecular Mass (Molecular Weight) of Hydrocarbons by Thermoelectric Measurement of Vapor Pressure, and
(B) ASTM D2502 - 04(2009), entitled Standard Test Method for Estimation of Molecular Weight (Relative Molecular Mass) of Petroleum Oils From Viscosity Measurements,
(ii) ASTM D5291 - 10, entitled Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Petroleum Products and Lubricants, and
(iii) if no such ASTM standard applies, an applicable internationally recognized method, and
(c) for a gaseous fuel,
(i) in accordance with either of the following ASTM standards that applies for the measurement of the carbon content of the fuel:
(A) ASTM D1945 - 03(2010), entitled Standard Test Method for Analysis of Natural Gas by Gas Chromatography, and
(B) ASTM D1946 - 90(2011), entitled Standard Practice for Analysis of Reformed Gas by Gas Chromatography, or
(ii) by means of a direct measuring device that determines the carbon content of the fuel;
- i
- is the ith sampling period referred to in section 27, with “i” going from the number 1 to n, where n is the number of those sampling periods; and
- Qi
- is the mass or volume, as the case may be, of the fuel combusted during the ith sampling period, expressed
(a) for a solid fuel, in tonnes, on the same wet or dry basis as the one used in the determination of CCA,
(b) for a liquid fuel, in kL, and
(c) for a gaseous fuel, in standard m3.
- Date modified: